MegLIFE
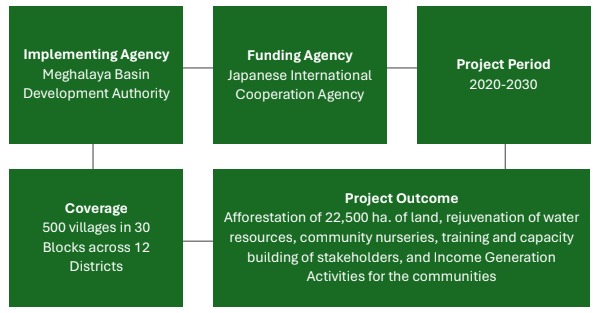
PROJECT FOR COMMUNITY-BASED FOREST MANAGEMENT AND LIVELIHOODS IMPROVEMENT IN MEGHALAYA
In 2017, Meghalaya's forests constituted 76.4% of the state's total area but faced degradation, with a 1.2% decrease (142 km2) in forest area and a 157 km2 increase in open forest rate to 42% from 2013 to 2017. This degradation resulted in adverse impacts such as reduced timber and non-timber forest production, soil erosion, and river sedimentation, which has negatively affected local communities. To address these issues, the Project for Community-Based Forest Management and Livelihoods Improvement in Meghalaya (MegLIFE) was initiated, aligning with the state's "Meghalaya Vision 2030." MegLIFE aims to restore and conserve natural resources, enhance livelihoods, strengthen institutions in project villages, and contribute to environmental conservation, biodiversity, and socio-economic upliftment in Meghalaya. It supports sustainable community forest management, participatory planning, and inclusive growth in line with regional and national development objectives including the North Eastern Region Vision 2020 and the "Green India Mission" under the National Action Plan on Climate Change.
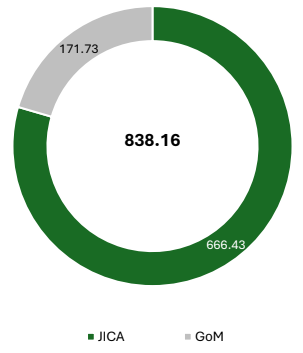
Financial Pattern - INR Cr
-
COMPONENT 1: SUSTAINABLE FOREST MANAGEMENT
Sustainable Forest Management includes planning and implementation of core forestry operations Major sub-components includes grass-root planning of forestry operations; implementation of forest working plans for individual forests units; planning and development of village level community nurseries and nurseries management by Forest and Environment Department and Autonomous District Council; soil and water conservation measures; fire management in fire-vulnerable forest areas; development of critical infrastructure for forest management.
-
COMPONENT 2: COMMUNITY DEVELOPMENT AND LIVELIHOOD
Community Development and Livelihood supports forest-based livelihoods and enterprise development for enhanced incomes of communities from forest management. This component is designed to provide sufficient incentives for community participation in sustainable land and water management.
-
COMPONENT 3: INSTITUTIONAL STRENGTHENING
Institutional Strengthening addresses institutional capacity gaps of the implementing agencies with assessment, reforms, training and capacity building, supply of equipment, hardware and software, provision for professional support, development and implementation of social and environmental framework, knowledge management and communication etc.

